Argentina -- School-age
Argentina
Things to Know
Official Name: Argentine Republic
Capitol City - Buenos Aires
Buenos Aires is the most European city in Latin America, full of ornate French style buildings fronted along tree lined boulevards with fountains, parks and sidewalk cafes.
Britannica Video: Explore the many faces of the city of Buenos Aires, Argentina
County's inhabitants: Argentine
Abbreviation: AR
Currency of Argentina: Peso.
Native Language: Spanish.
Official Religion: 90% of the population is Roman Catholic. The population is principally of European descent, especially of Italian and Spanish origin.
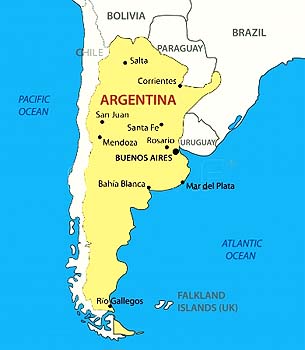
Argentina is a fascinating triangular shaped country located along South America's east coast.
It is the eighth largest country in the world.
Argentina is South America’s second largest nation. Brazil is the largest country in South America.
Argentine Government
Argentina is a federal republic with two legislative houses the Senate and Chamber of Deputies. The executive branch is headed by the president. The President of Argentina acts as Head of State and leads the executive branch.
In 1976 the military took over the elected civilian government, an event that has often occurred in Argentine history. This military dictatorship ended after the disastrous Falkland Islands War, a brief undeclared war fought between Argentina and Great Britain in 1982. Civilian government rule returned in 1983 and the constitution of 1853 was restored.
National Symbols of Argentina

The Argentine flag is a triband consisting of two bands of light blue (celeste meaning sky blue), with a white band between, and a yellow sun in the middle.
The Argentina flag became the official flag in 1812. It was created by General Manuel Belgrano during Argentina's War for Independence from Spain. In 1818, the gold "Sun of May" was add to the center of the flag, a reference to event of the May Revolution of 1810 when it has be said that the sun shone through the clouds
Today's Argentina's flag became official in 1861.
The most popular understanding is that the colors represents the sky, clouds, and sun. The middle sun on the flag was from the first Argentine coins. It is also thought that the pale blue (celeste) is from the cockades (a decoration that is worn on a hat especially as part of a uniform to show a persons rank).

National Bird: Rufous Hornero
It is also known as the red ovenbird for its oven-shaped nest.

National Flower: Ceibo (Erythrina crista-galli)
Animals
Argentina has a great variety of animals.
Found in the Gran Chaco region are jaguars, deer, monkeys, tapirs, and the puma the second largest cat in the Americas
The Margay, also known as the Long Tailed Spotted Cat.
The Pampas Cat or Grass Cat
Guanacos (llamas)—Related to camels
The Andean Condor
Magellanic Penguins in Patagonia are the largest of the warm-weather penguins. These penguins were named after Ferdinand Magellan who first saw them in 1519 on his first voyage around the tip of South America. They live on the coast of Argentina, Chile and the Falkland Islands.
Explorers
In 1502, Amerigo Vespucci was an explorer during the Age of Discovery. During his expedition Vespucci was the first to recognize North and South America as distinct continents and not a landmass in Asia.
Juan Díaz de Solís a 16th-century navigator and explorer of the Río de la Plata in 1516.<
Pedro de Mendoza in 1536 founded the first settlement of the present Buenos Aires.
Climate
Argentina's climate ranges from hot and humid in the north through humid and steamy in the center to cold in the south. The seasons are reversed from the Northern Hemisphere.
Land
Argentina may be divided into six geographical regions: the Paraná Plateau, the Gran Chaco, the Pampa (see under pampas), the Monte, Patagonia, and the Andes Mts.
Video
In Northern Argentina the Gran Chaco is a predominantly flat alluvial plain with a subtropical climate. The region is seasonally flooded, and marshlands remain for long periods during the year because of poor drainage. In the western Gran Chaco are scrub forest dominated by carob trees.
South of the Gran Chaco is the Pampa, a vast natural grassland The Pampa's deep, rich soil is the basic wealth of the country. The “Wet Pampa,” the more humid eastern part of the region, is Argentina's principal agricultural area and produces most of the nation's exports. It is the granary of South America, with wheat, alfalfa, corn, and flax the principal crops. Cattle ranching is prevalent throughout the Pampa and especially in the southeast and north; sheep are also raised there. Most of the principal cities of Argentina and most of its industry are found in the Pampa region.
The Monte, an arid region in the rain shadow of the Andes, has natural vegetation varying from short grasses in the east to cacti in the west.
The Andes Mountains are one of the longest and one of the highest mountain ranges in the world it stretches along the entire west coast of South America from Cape Horn to Panama and Venezuela- 7,250 kilometers (4,200 miles). Most of the highest mountains in the Andes are volcanoes, some still active, many dormant or extinct.
Southernmost Argentina (and Chile) are known as Patagonia, a largely uninhabited wilderness with dense rainforest and rugged peaks.
Tierra del Fuego is an archipelago (or a group of islands) shared with Chile, at the southern tip of South America. Its capital, Ushuaia, is the world's southernmost city.
People
José de San Martin was a South American military hero who fought to win the independence of Argentina, Chile and Peru.
Juan Peron was a dictator who ruled Argentina in the 1940s and 1950s and again briefly before his death in 1973.
Peron’s wife Eva (nicknamed Evita or Little Eve) virtually co-governed the country during his first six years as president
Things to Do
Read: "The Magic Ball"
A witch lures a young girl into a terrible trap with a magic ball. Her brother, along with some magical creatures, pool their efforts to rescue her.
Make
La Boca is a neighborhood in Buenos Arires, Argentina, it is a popular for it’s bright and colorful houses.
Fun Facts
Biggest Dinosaur believed found in Argentina.
Christ of the Andes, statue of Christ commemorating a series of peace and boundary treaties between Argentina and Chile. Dedicated Mar. 13, 1904, it stands in Uspallata Pass, high in the Andes, on the Argentine-Chilean boundary.>
See Also