India -- School-age
India
Things to Know
Bharat (in Hindi) and Republic of India (in English).
It is a federal republic of southern Asia and a member of the Commonwealth.
Capital: New Delhi
India is the second most populated country in the world with over a billion people.
Currency:
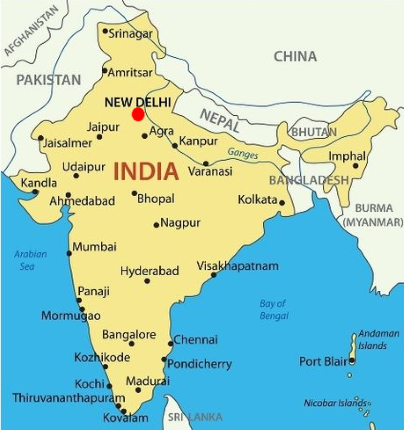
The India subcontinent is a peninsula that juts southward from Asia into the Indian Ocean. The Indian subcontinent: a large area of land that is part of a continent; a major subdivision of a continent.
National Symbols

The state emblem is an adaptation from Ashoka's Sarnath Lion Capital.
National Bird - Peacock
National Animal - Tiger
National Flower - Lotus
National Fruit - Mango
National Tree - Indian fig tree (Indian Banyan)
National Anthem - Jana-gana-mana
National Song - Vande Mataram
Animals
Many zoologists estimate that there are some 76,000 species of animals in India. The best-known of India's animals are the Indian elephant and the tiger.
Two of India’s most impressive animals, the Bengal/Indian Tiger and the Asiatic Elephant are found in most regions of India.
(fact sheet). Tigers are India's Official National Animal and India's largest cats. Other cats of India include four species of panther--the ; the ; the rarely seen albino leopard; and the , which is found only in the Himalayas.
Domesticated elephants are often used instead of bulldozers or tractors to build buildings and clear jungle or forest.
The Indian elephant is a sub-species of the Asian elephant.
Elephant Species Differences
In India, monkeys are treated as very special animals, sometimes they are even considered holy. the monkey deity.
The commonest species of monkeys found in India are the and the , a type of langur. Another type of monkey, the or wanderoo, is found in a small area of southern India.
-India'sNational Bird
(India's only ape)
/ Chinkara-The smallest asiatic antelope.
look more like raccoons than their closest relative - the giant panda. (Eastern India's Himalayan Mt.)
(now found only in the Gir Forest of Saurashtra, Gujarat)
India has more than 400 species of reptiles and snakes.
Cobras-The longest venomous snake
For more information on Cobras visit the
India has 90 species of scorpions.
-learn about these venomous arthropods.
Climate
India has a lot of huge earthquakes, floods, and droughts.
Most of India has three seasons: cool, hot, and rainy. From March to the end of June is the hot season. During the hot season parts of the southern plateau remain cool and the northern mountains are cool or cold, depending on the altitude. Cyclones often bring storms to the coastal plains at this time.
From June to September is the rainy season when (violent seasonal winds) blow across the Indian Ocean. A mild winter lasts from October to February.
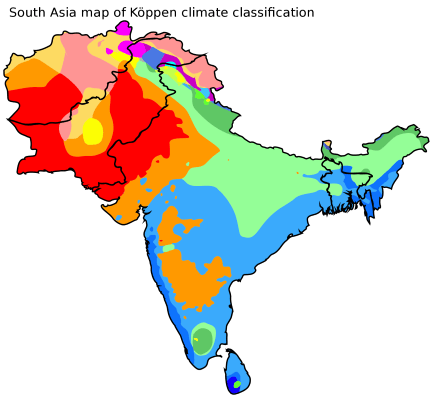
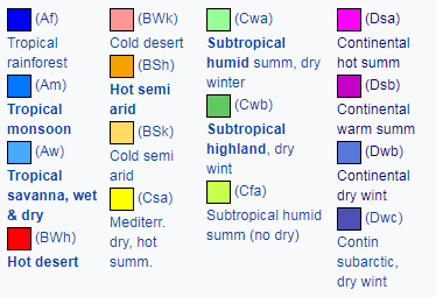
Land
Because of its size, India is home to a wide range of different environments, from high, snow-capped mountains to tropical rainforests and from hot and cold deserts and scrubland to lush, fertile plains and valleys.
Three main geological regions of India are:
North India - Indo-Gangetic Plain and the Himalayas.
Peninsula or South India
The Indo-Gangetic Plain is most of the northern and eastern section of India. In this plain are many rivers, such as the Ganges River and the Indus River valley.There are large urban areas and fertile plain.
The Himalayas the highest mountains in the world. It includes the highest mountain, Mount Everest.
The Peninsula (South India) is bordered by the Arabian Sea, the Bay of Bengal, and the Indian Ocean.
The Himalayas - Mount Everest

Aerial photo Mount Everest from the south.
The Himalayas are the highest mountains on earth, towering more than 8000 meters. The tallest peaks of the Himalayas are always covered with snow. The word Himalaya means "the home or abode of snow." No plant life grows near the mountain's peak due to powerful winds, extremely cold temperatures, and a lack of oxygen.
The Himalayas include Mount Everest, the tallest mountain in the world which is on the border between Nepal and China.
Taj Mahal
is the most well preserved and architecturally beautiful tomb in the world located in Agra in Northern India.
online with 360 degree photographic panoramas.

Taj Mahal
Plants
National Fruit of India-
Almost every plant family in the world is represented in India.
In southern India, grow various kinds of palm. Tropical plants grow in western India. Commercial crops of the region include bananas, betel nuts, cardamon, citrus fruit, coconuts, coffee and tea, ginger, pepper, and rubber. Ironwood, rosewood, and teak are plentiful in the broadleaf forests of the region.
One of India's most rare and treasured aromatic trees is the .
The bark of the contains quinine, a substance used to combat malaria. is a tropical disease carried by mosquitoes.
In northern India, grow a wide variety of broadleaf trees, such as alder, birch, laurel, and maple, and conifers. The area is also known for its rhododendrons, bamboo, and dwarf willow. Juniper, silver birch, and silver fir are abundant in the uppermost, alpine environment of the western Himalaya. Further down the mountain slopes grow forests of spruce, silver fir, and deodar (East Indian cedar).
Sal forests dominate the lowest regions and the Ganges region, providing a wood much used in the furniture industry. Tall grasses and forests of bamboo grow in the Brahmaputra and Surma valleys of Assam. Assam is also one of the original homes of the mango, a commercially important fruit of south and east Asia. In the valleys of the Himalaya, farmers grow apple, apricot, peach, pear, and walnut trees.
Languages
One of the main India has a total of 1652 different languages and dialects.
Hindi and English are the co-official national languages of India. In addition, the Indian government recognizes 18 languages as official; Hindi is the most widely spoken.
Official
Read
Legend on the beginning of the Ganges River.
life was dedicated to the ideals of Truth, Non-violence and Love. He was the architect of India's freedom and one of the greatest men of the 20th century.
The
Caste System
Castes are unchanging social groups. A person born into one caste can never change caste or mix with members of another caste. The Caste System has been illegal in India for more than fifty years.
Games
(age 8 +)
Chess was invented in India. Learn and play chess at free online academy.
Religions
Religion plays a vital role in the Indian way of life. Religious laws of the Hindus and Muslims govern the people's clothing, food, and marriage. They also strongly influence the type of occupation among persons who strictly follow the laws.
India is a secular country (there is no official religion) and is home to peoples of many different faiths: Hinduism , Islam, Christianity, Buddhism , Jainism , Sikhism, Zoroastrianism, Judaism, and other innumerable religious traditions. Hinduism is practised by over 80% of the population.
- A Hindu festival observed all over the North. It heralds the end of winter.
- Every region observes this 10-day festival. It symbolizes the triumph of good over evil.
, the Festival of Lights

Henna Hand - Children trace their hand and decorate.
Rangoli color pages and crafts. Rangoli is a traditional Indian art form consisting of patterns, during many festivals it is used to decorate a floor.
Video
Sites to See
India: The Living Arts - Canadian Museum of History (Includes teacher guide)
Recommended Books