Venezuela (South) -- School-age
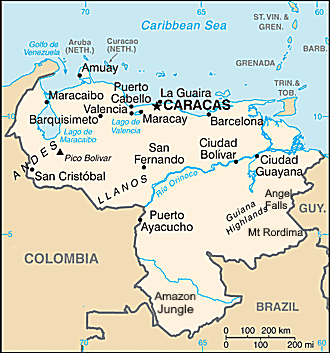
The Guyana region in southern Venezuela includes the Guiana highlands and parts of the Amazon rainforest.
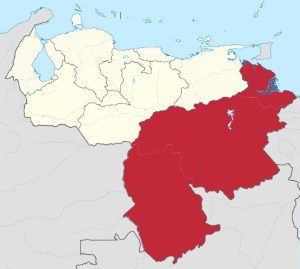
Guayana Region Venezuela
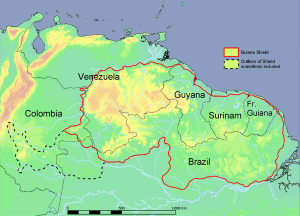
The Guiana Shield is an extensive heavily forested land area with granitic mountains, savannahs, rainforests, and many rivers that coverers half of southern Venezuela and extends into French Guiana, Surinam, northern Brazil, and southeastern Colombia. The higher elevations are the Guiana Highlands, with flat-topped mountains (tepes) and the source of some of the world's most spectacular waterfalls.
The Guiana Highlands in Venezuela are located north of the Amazon and south of the Orinoco River. The Orinoco River is the second largest river in South America (the Amazon is the largest), at a length of 1,330 miles (2,140km). The river is shared by Venezuela and Colombia with 76% of the river in Venezuela.

Mount Roraima
Canaima National Park in south-east Venezuela is immense covering an area of 30,000 sq km. It includes flat-topped mountains and Angle Falls.
A tepui is a flat-topped mountain or mesa found in the Guiana Highlands of South America. Mount Roraima is the highest point in Guyana at about 9 miles long (14 km) and 9,094 feet [2,772m) high. It is where the where the boundaries of Brazil, Venezuela, and Guyana meet. About 85% of Mount Roraima is located in Venezuela.
On the top of the tepui (mesa) it rains almost every day which washes away most of the nutrients that plants need to grow, creating a unique landscape of bare sandstone with only bushes and algae present. This also creates some of the highest waterfalls in the world as water flows over and down the sides of the mountains.
Kaieteur Falls in Guyana is the world's largest single drop waterfall. Kukenaam Falls is the second tallest major waterfall in Venezuela.
Angel Falls in Venezuela is the worlds highest waterfall is in the Guiana Highlands. Angel Falls is the world's highest and longest uninterrupted waterfall, with a height of 979 m (3,212 ft).

Angel Falls
Venezuela's Ancient Tepuis Video
Indigenous People
Venezuela's indigenous people in the Orinoco and Amazon regions have lived long before recorded time.
In the Southern Venezuela region several tribes live in the area: Piaroa, Pemon, and Yanomami.
The forested islands which make up the delta on the northeast coast are home to the Warao people, who live on the riverbanks in houses on stilts.
Explorers
Alfonso de Ojeda and the Florentine, Amerigo Vespucci discovered the mouth of the Amazon and Orinoco Rivers in South America. Native huts built on piles above the lake reminded Vespucci of Venice, thus leading him to name the discovery Venezuela, or Little Venice.
Baron Alexander von Humboldt - Explorer and Naturalist
People
Simon Bolivar - The man who won independence for Bolivia, Panama, Colombia, Ecuador, Peru, and Venezuela.

Simon Bolivar statue in Caracas, Venezuela
Climate
The climate is warm, rainy and humid, with a very thick vegetation.
Plants
Tropical Rainforest products in daily use.
Animals
There are a variety of animals in the tropical jungles, mountains, savannhas, and rivers of Southern Venezuela. Some of the animals include: mountian lion. ocelot,, tapir, armadillo, anteater, and the longest snake in the world the green anaconda.

Orinoco crocodile
The Orinoco crocodile is found in the Orinoco River basin and freshwater rivers in Colombia and Venezuela.
Jaguar, the largest cat of the Americas.
Silky Anteater, the smallest living anteater that is a tree-climbing anteater with golden fur and a long prehensile tail.
10 AnimalsThat Live In Venezuela
Green Anaconda Song Video
Things to Do
Where's The Amazon? interactive.
The Amazon spreads across significant portions of the countries of South America: Bolivia, Brazil, Colombia, Ecuador, Peru, and Venezuela