China -- School-age
China
Do not want others to know what you have done?
Better not have done it anyways.
-Chinese Proverb
I Hear, and I Forget
I See, and I Remember
I Do, and I Understand
-Chinese Proverb
Click to print the above Chinese Proverb
Capital: Beijing
China is a country in East Asia bordering fourteen other countries. Mongolia on the north; Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Tajikistan, Afghanistan, and Pakistan on the west; and India, Nepal, Bhutan on the southwest, Myanmar (Burma), Laos, and Vietnam on the south; North Korea on the southeast and Russia on the northeast. It faces South Korea and Japan across the Yellow Sea and the Philippines across the South China Sea.
China is the most populated country in the world with over one billion people. It is the third largest country in the world, after Russia and Canada.
Land

Gobi Desert Autonomous Region China
China has great physical diversity. The eastern plains and southern coasts is lowlands and foothills. This is where most of China's population and argricultural land are located.
The southern areas of the country (South of the Yangtze River) are hilly and mountainous. The Yangtzee River is the world's third longest river. The Himalayas, the world’s tallest mountains, are along China’s southwestern border with India.
In the west and the north are rolling plateaues and sunken basins such as the Gobi Desert and the Taklamakan Desert (one of the driest spots on Earth).

Mt. Everest North Face Toward Tibet
China's History
China's culture and civilization goes back thousands of years.
The Origins of Chinese Civilization (2200 - 221 BCE)
Hsia (2200-1766 BCE)
Shang (1766-1040 BCE)
Advances during the Shang dynasty: Invention of bronze (Beginning of the Bronze Age 1600BCE) and oracle bones. Bronze is still used today.
Video: KS2 Prehistory – The Bronze Age How bronze is made by combining copper and tin.
Chou (Zhou) (1100 BCE-221 BCE)
The Zhou dynasty ruled in China longer than any other.
The Zhou dynasty gave birth to a golden age of philosophy.
Taoism and Confucianism both developed during the Zhou reign. According to legend, Taoism was founded by a man named Lao-tzu (Lao Zi), who was born around 604 BCE.
Video
The Early Empire (221 BCE - 589 CE)
Ch'in (Qin) (221BCE-206 BCE)
During the Qin dynasty, all of China was united and the Great Wall of China was begun.
Qin Shihuangti was the first emperor of China. In 1974, Emperor Qin Shihuang's tomb was discovered, it included 6,000 terra cotta army figures. Qin Shi Huang, the emperor who founded the Qin Dynasty.
Terra Cotta Warriors-The Underground Army -- Clay warriors made by a sixth grade class.
The building of the Great Wall of China begins. It is designed to keep out a destitute and starving people, the nomadic Hsiung Nu.

Crayola Build the Great Wall. Build the Great Wall of China using tissue boxes.
Great Wall Of China Video
Han (206 BCE-220 C.E.)
The Han dynasty was known for conquering new lands and expanding trade.
The Han dynasty fell in C.E. 220. But even today, people in China call themselves "Han people" in honor of this time of accomplishment.
Han accomplishments included:
Chinese scientists created the world's first compass and the first simple seismograph, or earthquake detector.
There were many earthquakes during the Han Dynasty so they invented a seismograph. The urn-like Houfeng Seismograph was invented by Zhang Heng.
Replica of Zhang Heng's
seismoscope
The seismograph was an ornamental vessel of cast bronze, consisting of eight dragons facing outward in a circle. Each dragon gingerly held a ball in its jaws.
The instrument was designed so that any seismic tremor would cause the ball to fall from the jaws of the dragon facing the direction of the tremor. The ball fell in the direction that the earthquake was coming from so it also told the people which way the earthquake was.
Many kinds of medicine, including acupuncture and the use of herbs. Advances in engineering and mathematics. The invention of paper, exceptional works of art and writing.
Tsai
Lun is created with the inventor of paper. Porcelain and the world's first wheelbarrow.
50-70 CE Buddhism arrives in China around this time.
The Second Empire (589 CE - 1644 CE)
Sui (589CE-618 CE)
Tang (618CE-907 CE)Empress Wu Zetian (only female empress)
Song (960CE-1279CE)
During the Song Dynasty numerous things were invented. The Sond Dynasty is sometimes referred to as China's Age of Invention.

The Mongolian Empire (1206 CE –1368 CE) was perhaps the largest empire in human history in terms of geographical expanse. It extended west to east from Poland to Siberia, and north to south from Moscow to the Arabian peninsula and Siberia to Vietnam.
Yuan was the shortest lived of the major dynasties.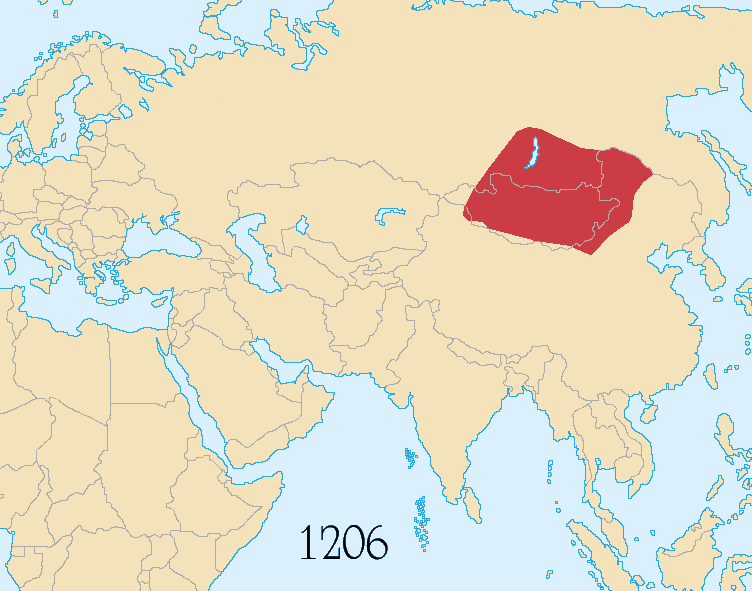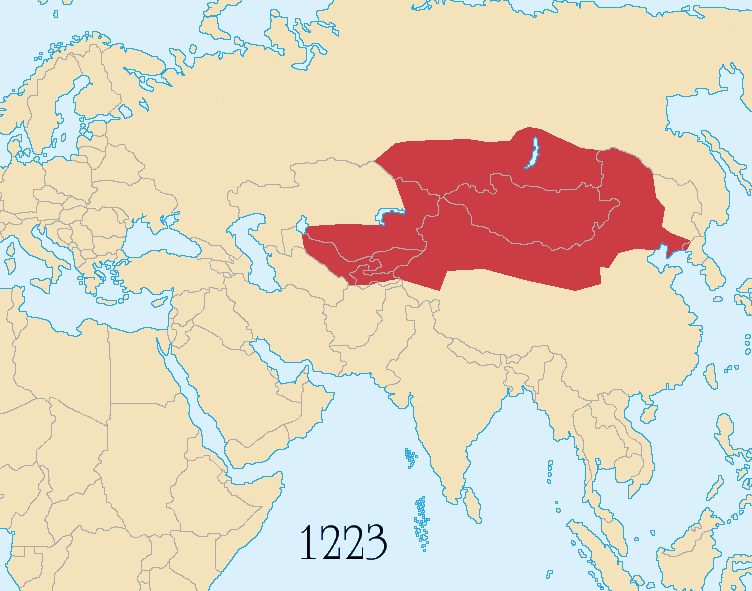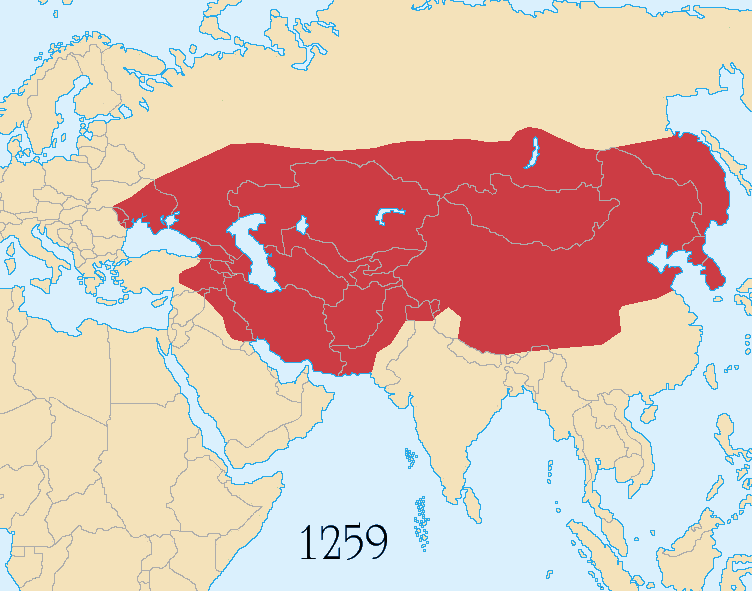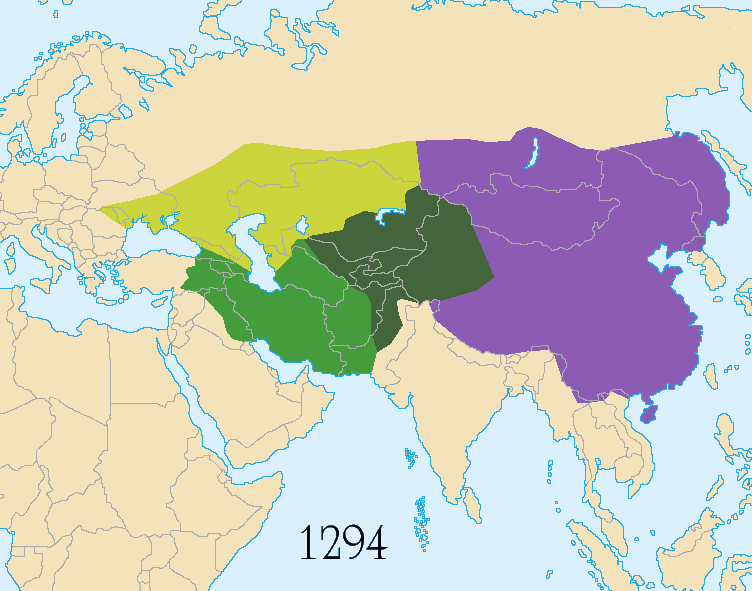
Yuan (Mongol) (1279 CE -1368CE)
Ming (1368 CE -1644CE)
Genghis Khan

Genghis Khan
The achievements of Genghis Khan were grandiose. He united all the Mongolian nomadic tribes and united the nomadic tribes in a disciplined military state. Genghis Khan led his united Mongol hordes out of Mongolia to create an empire unequaled in land area even by Alexander the Great.
The destruction brought about by Genghis Khan survives in popular memory. No one knows exactly how many people were slaughtered by his destructive raids. Historian R. J. Rummel at the University of Hawaii, estimated that 30 million people were killed under the rule of the Mongol Empire, and the population of China fell by half in fifty years of Mongol rule.
These conquests of Genghis Khan were but the first stage of the Mongol Empire, the greatest continental empire of medieval and modern times.
His successors would extend their power over the whole of China, Persia, and most of Russia.
Sites to See
National Geographic's Genghis Khan
Kublai Khan

Kublai Khan
In 1279, Genghis Khan's grandson, Kublai Khan, founded the Chinese-style Yuan dynasty. He conquered China, becoming the first emperor of the country's Yuan Dynasty. Mongol rule brought relative peace to Asia, leaving China accessible to foreign visitors, such as Marco Polo.
Ming Dynasty (1368-1644)
During the Ming dynasty the Great Wall of China was completed and the Forbidden City, the imperial residence in Beijing was built. The Ming dynasty is known for its blue and white Ming porcelains.

Ming Imperial
White Blue Vase











